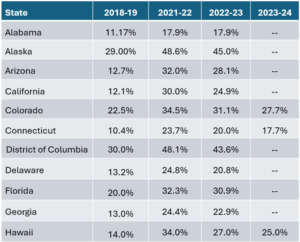
Chronic absenteeism is classified as students missing 10 percent or more of the school year for any reason. Despite slight improvements since the peak in 2021, post-pandemic absenteeism remains a major challenge for schools across the U.S. For instance, in the 2022–23 academic year, about 30% of districts reported chronic absenteeism levels between 20-30%, while nearly 10% faced levels above 30%. Although these numbers have begun trending lower than the pandemic highs, they still indicate persistent issues in student attendance that demand urgent attention.
Image: FutureEd State Chronic Absenteeism Rates, By School Year
View full report
Attendance Matters
Chronic absenteeism impacts not only individual academic success but also long-term graduation rates, especially for students who fall behind early. Missing key educational milestones, such as reading at grade level by third grade, significantly increases the risk of dropping out. As school leaders acknowledge, addressing absenteeism requires multi-faceted solutions involving families, educators, and the broader community.
Why Are Students Still Missing School?
- Health & Mental Health Issues: Ongoing challenges like chronic illnesses and mental health problems account for a significant portion of absences.
- Transportation Barriers: Limited transportation access, especially in rural areas or single-car households, continues to hinder students from attending school regularly.
- Disengagement: A cultural shift since the pandemic has affected students’ and families’ perception of schooling, with many now viewing it as optional. Additionally, experiences with bullying contribute to avoidance behavior.
- Family Responsibilities & Instability: Economic challenges like food insecurity, unstable housing, or the need to care for relatives add to the absenteeism problem, especially among marginalized communities.
Strategies to Combat Chronic Absenteeism
In August of 2024, an American School District Panel Survey found that 93% of districts have implemented at least one strategy to address absenteeism. However, one-quarter of these districts found their interventions were not effective. District leaders now suggest that schools need to adopt fresh, more engaging approaches to re-establish the importance of consistent attendance. Here are a few examples:
- Early Warning Systems: Many districts are now using early warning systems to flag at-risk students and intervene proactively.
- Mental Health Support: Districts are investing in mental health resources, recognizing that emotional well-being is essential for consistent attendance.
- Creating Welcoming Environments: Attendance Works emphasizes the importance of building engaging school cultures where students feel safe and connected. Schools need to reengage families and foster meaningful relationships to keep students coming back.
- Community Engagement and Carpooling Programs: Schools are increasingly turning to solutions like organized carpooling. Tools such as GoKid Connect facilitate safe family networks and provide dashboards to track attendance improvements, transportation savings, and environmental impact.
Benefits of Carpooling
- Increased Access to Transportation: Offers a reliable transportation option, especially valuable for students in remote areas or from single-vehicle households, both at greater risk for chronic absenteeism.
- Cost-Effective: Reduces the financial burden of commuting, particularly in states like California, where only around 10% of students have access to busing. Sharing rides offers an affordable alternative to solo commutes.
- Eases Traffic Congestion: Puts fewer cars on the road to help reduce congestion around schools, making drop-off and pick-up smoother and safer for everyone.
- Social Benefits: Provides a social platform for students, fostering friendships outside the classroom—a critical factor in addressing social isolation, which can lead to chronic absenteeism.
- Enhancing Attendance: helps improve school attendance by mitigating transportation barriers. Modern solutions like GoKid Connect even offer admin dashboards to track registration, carpools set up, miles saved, and CO₂ reduction, allowing schools to measure their impact on attendance rates.
Final thoughts
Comprehensive district-wide strategies are essential for long-term improvement. Schools must balance transportation solutions with engaging curricula and supportive environments to overcome student attendance challenges effectively.
In summary, chronic absenteeism in U.S. schools remains a pressing issue, demanding both systemic interventions and community involvement to drive meaningful change. Solutions like carpooling are just one part of the equation, requiring schools to adopt broader approaches for sustainable attendance improvements. By collaborating with organizations like Attendance Works and leveraging community resources, schools can effectively combat chronic absenteeism and ensure a positive and engaging educational experience for all students.
For more information on our district-wide school carpool program, please contact schools@gokid.mobi or book a free consultation here.



